ProPublica is a nonprofit newsroom that investigates abuses of power. Sign up to receive our biggest stories as soon as they’re published.
Vincent Gaynor remembers, almost to the minute, when he realized his part in birthing the breakthrough gene therapy Zolgensma had ended and the forces that turned it into the world’s most expensive drug had taken over.
It was May 2014. He and his wife were sitting in the cafeteria at Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus, Ohio.
Elsewhere in the hospital, an infant — patient No. 1 in a landmark clinical trial — was receiving an IV infusion that, if it worked, would fix the genetic mutation that caused spinal muscular atrophy, a rare, incurable disease. At the time, children born with the most severe form of SMA swiftly lost their ability to move, to swallow, to breathe. Depending on the disease’s progression, most didn’t live to their second birthdays.
The Gaynors’ daughter Sophia had been diagnosed with SMA five years earlier. Since then, they’d raced to fund research to save her. Their charity, Sophia’s Cure, was covering a substantial portion of the costs of the trial.
They’d helped raise about $2 million for a program at Nationwide run by Brian Kaspar, a leading researcher. Gaynor, a New York City construction worker, had forged a tight bond with Kaspar, speaking frequently with him by phone, sometimes deep into the night.
But their relationship had started to fray when — with success in sight — Kaspar became part owner of AveXis, a biotech startup that had snapped up the rights to his SMA drug. Billions of dollars were at stake.
When Kaspar walked into the cafeteria that day, Gaynor said, the scientist didn’t acknowledge him or his wife before sitting down a short distance away. Neither did the man with him, the startup’s CEO.
“It was like they didn’t know us,” Gaynor recalled.
When Zolgensma hit the market five years later, it was hailed as a miracle drug. Some babies treated with it grew up able to run and play. It helped reduce U.S. death rates from SMA, long the leading genetic cause of infant mortality, by two-thirds.
That leap forward came at a sky-high price: more than $2 million per dose, making Zolgensma then the costliest one-time treatment ever.
How did a drug rooted, like many, in seed money from the U.S. government — that is, American taxpayers — and spurred by the grassroots fundraising of desperate parents, end up with such a price tag?
The story of Zolgensma lays bare a confounding reality about modern drug development, in which revolutionary new treatments are becoming available only to be priced out of reach for many. It’s a story that upends commonly held conceptions that high drug prices reflect huge industry investments in innovation. Most of all, it’s a story that prompts, again and again, an increasingly urgent question: Do medical advances really have to be this expensive?
ProPublica traced Zolgensma’s journey from lab to market, from the supporters there at the beginning to the hired guns brought in at the end to construct a rationale for its unprecedented price.
We found that taxpayers and private charities like Sophia’s Cure subsidized much of the science that yielded Zolgensma, providing research grants and opening the door to federal tax credits and other benefits that sped its path to approval.
Yet that support came with no conditions — financial or otherwise — for the for-profit companies that brought the drug over the finish line, particularly when it came to pricing.
Vincent Gaynor with his daughter Sophia (Photo courtesy of Vincent Gaynor)Once Zolgensma’s potential was clear, early champions like the Gaynors were left behind as the private sector rushed in. AveXis’ top executives and venture-capital backers made tens or hundreds of millions of dollars apiece when the startup was swallowed by the pharmaceutical giant Novartis AG in 2018.
Wall Street analysts predicted Novartis’ new prize drug would be the first therapy to smash the million-dollar-a-dose mark. The Swiss colossus crafted a sophisticated campaign to justify more than double that amount, enlisting a team of respected academics, data-modelers and pricing strategists to help make its case.
“This was a case where the charities and the government did everything to get this thing commercialized, and then it just became an opportunity for a bunch of people to make transformative, generational wealth,” said James Love, director of the public advocacy group Knowledge Ecology International.
In a statement to ProPublica, Novartis said Zolgensma’s price reflects its benefits to children with SMA and to society more broadly.
“Zolgensma is consistently priced based on the value it provides to patients, caregivers and health systems,” the company said, adding that the drug may reduce the burden of SMA by replacing “repeat, lifelong therapies with a single treatment.”
Zolgensma’s price quickly became the standard for gene therapies. Nine of them cost more than $2 million. A tenth, approved in November, is predicted to run about $3.8 million, just shy of the most expensive, also approved last year, which costs $4.25 million a dose.
“Drug companies charge whatever they think they can get away with,” said David Mitchell, the founder of Patients For Affordable Drugs. “And every time the benchmark moves up, they think, ‘Well, we can get away with more.’”
Parents of children with SMA say their concerns about costs pale in comparison to the hope offered by such cutting-edge therapies. “I mean, it’s a child’s life,” said Hailey Weihs, who battled her health plan to get Zolgensma for her daughter. “Anybody would want that for their own child.”
The seven-figure costs of Zolgensma and other gene therapies add to the nation’s ballooning bill for prescription drugs, absorbed by all Americans in the form of rising insurance premiums and taxes for public programs like Medicaid.
Breakthroughs like Zolgensma are often framed as wins for all: Patients get life-saving new therapies. Drug companies and biotech investors make enough money to incentivize even more breakthroughs.
But not everyone’s a winner, Gaynor noted.
No one wanted Zolgensma to succeed more than he did, or understands better what it has meant for families like his. Yet his years behind the scenes of the drug’s development left him and his family disillusioned.
“I learned it’s all about money,” Gaynor said. “It’s not about saving people.”
When Vincent and Catherine Gaynor started their married life in 2006, they knew one thing for certain: They wanted children.
They learned well into Catherine’s 2008 pregnancy that they were both carriers for SMA, meaning there was a 25% chance their child would be born with the muscle-wasting disorder.
They were concerned but clung to the larger chance the baby would be born healthy.
When Sophia was born in late February 2009, at first they just marveled at her sweet disposition and bright, expressive eyes. How she loved being snuggled. How she sighed after she burped.
But it didn’t take long for Vincent, who’d grown up with younger siblings, to sense something was off. Sophia didn’t lift her legs. They flopped outward like a frog’s when he changed her diaper.
Their pediatrician assured them Sophia was fine. Then a different doctor suggested testing her for SMA. While they waited for the results, the family went to a nearby park, and Catherine pushed Sophia’s stroller around a pond. “I remember walking behind her with the video camera and knowing in my heart this was the last day we were all going to be happy,” Vincent recalled.
After Sophia’s diagnosis, Catherine quit her office job to care for the baby full time. Vincent started gulping down studies and going to conferences, desperate to find a way to save his daughter.
At the time, there were no treatments to slow or stop SMA. By the time Sophia was 4 months old, she needed a machine to help her breathe overnight. At 6 months, she could no longer take a bottle and needed a feeding tube. Each time she lost ground, their urgency to find a treatment grew.
The Gaynors didn’t have deep pockets or wealthy friends. He was a steamfitter with Local 638, from a family of steamfitters. They began raising small amounts of money by hosting golf tournaments and throwing Zumba parties. As the volume of donations grew, they founded Sophia’s Cure, emerging as serious players in the small world of SMA charities.
I learned it’s all about money. It’s not about saving people.
—Vincent Gaynor, who raised funds for medical research to help his daughter with spinal muscular atrophyVincent met Brian Kaspar at a cocktail hour for high-yield fundraisers. Kaspar was among the small group of top researchers working to find treatments for SMA, competing fiercely for recognition and funds. (Kaspar declined an interview request from ProPublica and didn’t respond to written questions.)
Because his drug was a gene therapy, public grant money and private philanthropy played an especially central role, with the National Institutes of Health alone putting over $450 million into science related to SMA. Drug companies at the time approached these treatments with more skepticism, waiting longer to invest and letting universities and academic hospitals do the heavy lifting, said Ameet Sarpatwari, an assistant professor at Harvard Medical School who studies the pharmaceutical industry.
Drug companies sponsored only 40% of the U.S. gene therapy trials active in January 2019, according to a study Sarpatwari co-authored.
“The narrative of industry is, ‘We’re doing the hard, expensive part of drug development,’ and, at least for cell and gene therapies, the most risky part is actually being done by public or federally supported labs,” Sarpatwari said, calling Zolgensma a “poster child” for the study’s findings.
By the time of the cocktail party, Kaspar had turned early research into a promising drug therapy that he was beginning to test on animals — the precursor to a human trial. Gaynor remembered him as humble and almost classically nerdy, happy to spend hours on the phone explaining how motor neurons work.
More established SMA charities tended to hedge their bets, spreading money around to multiple programs. But Sophia was already around 18 months old, and Gaynor had no time for that. In September 2010, when Sophia’s Cure won a $250,000 grant from the Pepsi Refresh Project by amassing votes online, he steered the money to Kaspar’s program. The following June, the charity signed an agreement promising Kaspar up to $1 million more, for which it had launched a drive to recruit 200 people to raise $5,000 apiece.
As the money flowed in, Gaynor and Kaspar became close friends. The Gaynors stayed overnight at Kaspar’s house on their drive to an annual charity event. Kaspar did a Q&A for the Sophia’s Cure YouTube channel from the Gaynors’ dining room and proofread posts Vincent wrote for the charity’s website.
Gaynor said they often talked about how getting the drug through the development process would require way more money and muscle than the various SMA charities could muster. Kaspar shared his conversations with venture capital firms and even asked Gaynor to talk to a potential investor.
Yet Gaynor said he was blindsided when Kaspar told him he’d formed a relationship with a Dallas startup called BioLife Cell Bank that had been focused on stem cell research.
The CEO, John Carbona, then 54, had run medical device and equipment companies, but he had no background in drug development. In an interview, Carbona told ProPublica that he took the reins at BioLife in the aftermath of his mother’s death, determined to do something “significant” to fulfill her hopes for him. After an associate’s twins were born with SMA, he said he became convinced that Kaspar’s gene therapy was the answer.
Carbona remade BioLife into AveXis: Av for adeno-associated virus serotype 9, the engine of Kaspar’s drug; ve for vector; X for the DNA helix; and Is for Isis, the goddess of children, nature and magic.
Still, for much of the next year and a half, money from charities and more than $2.5 million from the National Institutes of Health remained Kaspar’s bread and butter. In late 2012, Sophia’s Cure agreed to provide another $550,000 for a Phase 1 clinical trial. The Nationwide Children’s Hospital Foundation, an affiliate of the hospital, agreed to match it.
Kaspar singled out Sophia’s Cure for the extent of its support in a Nationwide press release.
“Sophia’s Cure Foundation has been the lead funder of this program and their incredible investment in this lab has accelerated our program by many years,” he said.
The trial protocol called for Kaspar’s therapy to be tested on infants up to 9 months old. It was a pragmatic decision: The company had limited funds and capacity to produce the test doses, which would be smaller for children who weighed less. Plus, the youngest children were likely to show the most dramatic results since they’d be treated before SMA inflicted its worst damage.
That left out Sophia, as well as most of the kids whose parents made up Gaynor’s fundraising network.
Gaynor’s dream of saving his daughter had tapered into determination to stop the disease’s progression and preserve the strength she had left. Sophia could no longer move her whole hand, but she could still tap with her right pointer finger. She could use an eye-gaze computer to click open screens and attend school remotely. She could communicate a bit, blinking once for yes and twice for no.
Early on, Gaynor said, Kaspar had promised a trial for older kids. But Gaynor felt Kaspar’s commitment wavered as his ties to AveXis grew and his reliance on funding from Sophia’s Cure diminished.
Carbona struck a deal with Nationwide Children’s in late 2013, getting AveXis the exclusive right to develop an SMA treatment using the hospital’s inventions, including Kaspar’s, in exchange for stock. A few months later, Kaspar signed a contract that granted him an even larger stake in the company. The company also landed its first major investor, Paul Manning of PBM Capital.
Over this period, Gaynor said, the phone calls and updates from Kaspar slowed. The Gaynors were invited to Nationwide Children’s for the start of the clinical trial by the family of the child receiving the first dose.
After the initial awkwardness in the cafeteria, the Gaynors said, Kaspar and Carbona eventually came over and sat with them. Carbona remembers it differently, saying that he recalled seeing the Gaynors that day and the mood was friendly, even celebratory.
Tension surfaced two months later when they all converged in Lancaster, Wisconsin, for Avery’s Race, an annual SMA fundraiser benefiting Sophia’s Cure.
The event brought together dozens of families from across the country for an awareness walk, an auction and a rubber ducky race in a nearby creek. In the finale, parents posed questions to Kaspar, Gaynor and Carbona, almost all of them about the clinical trial.
In video footage captured by a documentary filmmaker, Catherine Gaynor asked bluntly whether testing the drug only on infants meant the FDA would approve the treatment only for the youngest patients while “everyone else is left hanging out to dry.”
Kaspar acknowledged this was possible. He described expanding the treatment to older children as “step two” but made clear that funds for testing would have to come from Sophia’s Cure.
That’s what the money raised at Avery’s Race would support, Vincent Gaynor said, adding pointedly that his nonprofit would focus on the work others would avoid “because it’s not going to push stock prices up.”
Neither Kaspar nor Carbona responded directly to the dig. Carbona, noting the company had other funding needs, said they would expand testing when they had proof the drug worked.
I mean, they all have their hearts in the right place, but they’re being run by people who are looking for a return on investment.
—John Carbona, former CEO of AveXisBy early 2015, AveXis had raised millions from deep-pocketed biotech investors, adding members of several venture-capital funds to its board. Their participation would be critical in bringing the drug to market, paying for licenses to patented technology needed to make and administer it, for example. It also meant that Zolgensma had to do more than save lives — its promise had to make AveXis’ investors a profit.
Almost immediately, Carbona said, the board pushed to take the company public.
“I mean, they all have their hearts in the right place, but they’re being run by people who are looking for a return on investment,” he said.
As AveXis moved toward an initial public offering, some on the board questioned whether Carbona should continue running it, he said. He’d been accused years earlier of fraud and breach of fiduciary duty by a former employer, who won a $2.2 million court judgment against him. Carbona had denied any wrongdoing and the judgment was reversed in part and reduced on appeal, but the case left lasting damage. “It hurt me immensely,” he said.
Later that year, the board replaced Carbona with a new chief executive, Sean P. Nolan, who had a decadeslong record at pharmaceutical and biotech companies.
In September, a company representative offered the Gaynors a meeting with Nolan, saying Kaspar had stressed how instrumental Sophia’s Cure had been to the work on the drug. The Gaynors traveled into Manhattan for the meeting at a hotel bar. They told Nolan about their concerns, including that older kids wouldn’t have access to Kaspar’s drug since it hadn’t been tested on them. They said Nolan was cordial but never followed up. (Nolan didn’t respond to emailed questions from ProPublica.)
Nasdaq posted a video to Facebook with the caption, “Getting ready to ring the #Nasdaq opening bell with AveXis, Inc!” (Excerpt from archived live video clip obtained from Nasdaq/Facebook)Early the following year, AveXis went public. Nolan celebrated by ringing the NASDAQ opening bell as Kaspar, other company executives and members of the board whooped and clapped.
The IPO and subsequent stock sales raised hundreds of millions of dollars, but little of the money went toward additional trials on Zolgensma, an analysis by KEI, the public advocacy group, concluded.
The drug’s trials were small, often involving two dozen patients or fewer. AveXis, and later Novartis, spent less than $12 million up to the point of the drug’s approval — surprisingly little — to prove the therapy was safe and effective, the group estimated, based on information obtained through Freedom of Information Act requests, from studies and in Securities and Exchange Commission filings. (Novartis did not respond to questions from ProPublica about trial costs.)
The companies spent more than 10 times that amount to license intellectual property from others, KEI found. It’s not the clinical trials, Love, the director, said, that “makes developing gene therapies more expensive than it has to be.”
By the time of AveXis’ IPO, the Gaynors had decided to wind down Sophia’s Cure and step back from the SMA community. In 2015, Sophia began having seizures that became more frequent over time. She was 6 years old and growing weaker. Her SMA had progressed too far for Kaspar’s drug to help her.
Vincent’s sense of failure was crushing. In September 2016, after years of pent-up anger, he took a last stab at getting Kaspar and AveXis to acknowledge that the charity and its donors had essentially been a partner in developing Zolgensma.
Sophia’s Cure sued Kaspar, Carbona, Nolan, AveXis, Nationwide Children’s Hospital and its affiliated research institute and foundation for breach of contract. They’d relied on the charity’s money to advance the treatment, the lawsuit alleged, then violated the terms of donation agreements by cutting it out of credit and ownership rights once the drug was headed for success. The suit sought damages of $500 million.
Many larger disease foundations have launched venture philanthropy programs that invest in biotech companies and projects, getting royalties and other financial considerations if their gifts help fund new treatments. In court filings, Nationwide Children’s called the notion that the tiny Sophia’s Cure had any right to the drug “simply not true, or even plausible,” and AveXis called it “wholly unsupported.”
Carbona said he was “disappointed and surprised” by the lawsuit. Nationwide didn’t respond to questions about the matter.
In November 2017, as the litigation went on, the results of the clinical trial that the charity helped fund were published.
They were remarkable. At 20 months, all 15 children who’d been treated remained alive, and none relied on a ventilator to breathe. Eleven of 12 infants who received a higher dose of the therapy were able to sit unassisted, speak and be fed orally. Two could walk on their own.
Based on preliminary trial data, the FDA had designated Zolgensma a breakthrough therapy, one of three special designations that helped it race from human trials to regulatory approval in five years. Once the full trial results came out, AveXis became a red-hot acquisition target.
In April 2018, Novartis beat out another bidder, agreeing to buy the company for $8.7 billion.
The sale delivered massive windfalls to those with the biggest stakes in AveXis.
Kaspar alone took in more than $400 million. He swapped his longtime family home in New Albany, Ohio, for a 9-acre estate in San Diego County, California, that had been listed for just over $8 million. It featured a dine-in stone wine cellar, a horse ring and stables.
Nolan, who’d led AveXis for less than three years, walked away with over $190 million; according to a financial filing, his payout included a golden parachute worth almost $65 million. Manning, the startup’s first big investor, made more than $315 million, multiplying his original investment by about 60. (Manning didn’t respond to calls or emailed questions from ProPublica.)
Carbona, too, made a bundle — he declined to say how much. Since he’d already left the company, his payout wasn’t disclosed in SEC filings. “It didn’t matter,” he said of the money. The 20-hour days he’d put into AveXis had helped advance a lifesaving drug. “This was a significant impact on humanity.”
After watching AveXis’ executives and investors cash in, the Gaynors were dealt another painful setback. In early 2019, a U.S. district court judge in Ohio dismissed Sophia’s Cure’s lawsuit against all parties, concluding there had been no breach of contract.
Their last hope for recognition of the charity’s role in bringing Zolgensma to the world was extinguished.
Once Novartis acquired AveXis, it turned to setting a price for its much-anticipated gene therapy.
Unlike other nations, the United States allows companies to charge whatever they want for new drugs. This often means Americans pay the world’s highest prices, particularly during the period when only the original manufacturer can market a drug. Research by PhRMA, the trade group for drug companies, suggests unfettered pricing buys Americans faster access, as long as insurers will pay: New medicines most often launch first in the U.S.
Novartis’ deliberations took place at the end of a decade in which launch prices of new drugs had risen exponentially, drawing ire from patient advocacy groups and Congress. The median annual launch price for a new drug jumped from about $2,000 in 2008 to about $180,000 in 2021, one study found.
In part, the increase reflected that a growing proportion of new drugs treated rare diseases. Drug companies have argued these therapies should cost more because their markets are smaller, making it harder to recoup expenses.
Cell and gene therapies also drove prices higher. The first three such treatments were approved in 2017, launching at prices of $370,000 or more. Luxturna, a gene therapy for a rare disorder that causes vision loss, costs $425,000 per eye.
Industry insiders assumed Zolgensma would cost more than Luxturna. But how much?
There was what I would call pressure from Wall Street. This was going to set a precedent. Investors wanted to see a high price here.
—Dr. Steven D. Pearson, founder of a nonprofit that assesses drug pricesHow drug companies pick prices for their products is among their most closely held secrets.
Beyond its statement, Novartis didn’t respond to questions from ProPublica about how it set or justified Zolgensma’s price. We reached out to more than three dozen people who were at the company or consulted for it at the time; most didn’t respond or declined to comment. A couple said they were bound by nondisclosure agreements.
The most visible portion of Novartis’ work was an effort to put a dollar value on how much Zolgensma would extend and improve SMA patients’ lives and offset the costs of caring for them.
This approach, known as value-based pricing, was originally championed by insurers and consumer watchdogs hoping to rein in drug prices. Other nations use economic assessments to decide whether to cover drugs and at what price, often paying far less than the U.S. for the same treatments.
But pharmaceutical companies have learned to use these techniques to their advantage.
Novartis brought together experts from academia and top consulting firms to work with its internal health economics team to publish research framing Zolgensma as a good value even at a high price.
One of the academics was Daniel Malone, then a professor at the University of Arizona’s College of Pharmacy. The target audience was mainly insurers, he said in an interview.
“We’re trying to influence the thousands of pharmacy and therapeutics committees around the country that are going to be looking at this therapy and whether they are going to provide it,” he said.
At the company’s direction, Malone said, their model mainly compared Zolgensma to the only other SMA treatment then on the market, a chronic treatment called Spinraza. It, too, was pricey, costing $750,000 in the first year and $375,000 every year after; over a decade, the tally would come to more than $4 million. (This was hypothetical; the FDA had approved Spinraza in December 2016, so no one had ever taken it for that long.)
A paper Malone co-authored concluded that Zolgensma, at prices up to $5 million, was a better buy than its rival, delivering more therapeutic benefit at a similar cost.
Company executives publicly floated multimillion-dollar prices for Zolgensma using data points from Malone and others.
“Four million dollars is a significant amount of money,” Dave Lennon, then president of Novartis’ AveXis unit, told Wall Street analysts on a call in November 2018. But “we’ve shown through other studies that we are cost-effective in the range of $4 million to $5 million.”
Such talk normalized “prices that would’ve been inconceivable a generation ago,” said Peter Maybarduk, director of access to medicines at the nonprofit consumer advocacy group Public Citizen. “It has a desensitizing effect.”
Novartis’ team of experts also helped the company prepare for Zolgensma’s evaluation by the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review, a nonprofit that assesses whether drugs are priced fairly.
Unlike agencies in Europe that do similar evaluations to set drug prices for national health systems, ICER’s recommendations aren’t binding, but they’ve become increasingly influential among public and private payers when it comes to coverage decisions.
Dr. Steven D. Pearson, the nonprofit’s founder, said that as ICER began its review, he was aware that investors were pushing for a big number.
“There was what I would call pressure from Wall Street,” he said. “This was going to set a precedent. Investors wanted to see a high price here.”
At first, it looked like ICER would resist. Its December 2018 draft report said Zolgensma would be overpriced at $2 million.
Novartis pushed back. Another consultant, University of Washington professor emeritus Louis Garrison, submitted public comments echoing a forthcoming AveXis-sponsored journal article he’d co-authored. It argued that drugs like Zolgensma, which treat rare, catastrophic conditions, deserved higher prices, in part to “incentivize appropriate risk taking and investments” by their developers.
Garrison said AveXis reviewed the article prior to publication, but he had the final say on its content. “I thought I could make a value-based argument that they would welcome and that I believe in,” he said. He said he was not directly involved in the company’s pricing decision.
Nonetheless, ICER’s final report in April 2019 concluded Zolgensma would need to be priced under $900,000 to be cost-effective, though it acknowledged the drug was still being tested on infants who hadn’t yet shown symptoms of SMA. If they also benefited, the report suggested the drug’s value might increase.
On May 24, the FDA approved Zolgensma to treat children under 2 with all forms of SMA.
Novartis finally revealed the treatment’s U.S. launch price, $2.125 million, framing this as a 50% discount on Spinraza and what the company’s research showed the gene therapy was worth.
It also pocketed yet another taxpayer-funded benefit: a voucher from the Food and Drug Administration redeemable for accelerated review of another drug. Such vouchers — designed to encourage companies to invest in pediatric rare-disease treatments — can be sold, typically bringing prices of around $100 million apiece.
That same day, ICER released an update. New data showing Zolgensma’s substantial benefits for presymptomatic children made the drug cost-effective at prices up to $1.9 million by one benchmark and up to $2.1 million by another, it said.
Pearson acknowledged the scale and timing of the switch were unusual, but said it was driven by the data, not outside pressure. “We weren’t trying to fit into somebody’s preexpectation of where the number would be, believe me,” he said.
He immediately caught flak from insurers.
“I got a lot of phone calls saying, ‘Why on earth did you say $2.1 million was a fair price? How could that possibly be the case? We’re going to get swamped with this,’” he recalled.
The Gaynors, linking to news coverage on Zolgensma’s launch, wrote on the Sophia’s Cure Facebook page that they were “ecstatic” for children newly born with SMA, but that helping create the world’s most expensive drug “is certainly not what we had in mind.”
Malone said he thought it was mostly the potential for blowback that had prevented Novartis from demanding even more for Zolgensma. He’d recommended charging the full $5 million.
“Obviously it didn’t stick,” he said. “They decided not to price the product there, I think, because of the political backlash they would’ve gotten being the first out of the gate at that price point.”
In the months after Zolgensma hit the market in the U.S., parents of children with SMA frequently ran into resistance from health insurers that refused to pay for it.
Between late 2019 and mid-2022, Chicago attorney Eamon Kelly represented at least seven parents battling health plans across the country, helping them appeal denied claims or representing them at state Medicaid hearings.
Hailey Weihs came to Kelly when her insurer, a Medicaid-managed care plan in Texas, wouldn’t pay for Zolgensma for her infant daughter Aniya. As the coverage dispute dragged on, Aniya developed tongue tremors and lost the ability to bear weight on her legs.
Kelly won the case, as he had all the others, but Aniya’s five-month wait to get the drug was terrifying. “Every day kids with this disease lose motor neurons,” Weihs said. “When you lose them, you cannot get them back.”
Now state Medicaid programs and most employer health plans cover Zolgensma, but they often limit which patients get access. Some require doctors to get approval in advance before providing the treatment or impose restrictions on who’s eligible that go beyond what’s on the drug’s label, such as requiring an SMA specialist to prescribe it.
Though fewer than 300 American children are born each year with SMA, treatments for the disease annually rank among the top 20 drug classes for Medicaid spending. From 2019 through 2022, Medicaid spent $309 million on 208 Zolgensma claims, an average of almost $1.5 million per claim. (Under federal law, Medicaid doesn’t pay list price for drugs, getting substantial rebates; other payers also negotiate discounts.)
Globally, more than 4,000 children have been treated with Zolgensma, Novartis said. The drug topped $1 billion in annual sales in its second full year on the market. Through 2024, the company had reported over $6.4 billion in revenue from Zolgensma sales.
Novartis is working to expand use of the drug in older children, in part by seeking approval for a second version of the drug, administered by spinal injection, for children with less severe SMA.
“We are unwavering in our commitment to the SMA community and will continue to advance efforts to ensure access to Zolgensma for SMA patients who may benefit from this transformative, one-time gene therapy,” the company said in its statement.
Still, more than five years after Zolgensma’s approval in the U.S., the drug remains out of reach for children in many low- and middle-income countries.
Love, KEI’s director, said he’s heard from families in countries like India and South Africa, where it’s a struggle to obtain not only Zolgensma, but also other SMA treatments available in the U.S.
“It’s maddening to me,” he said.
After setting aside their charity work, the Gaynors refocused their energy on Sophia and her two younger siblings, who don’t have SMA.
The Gaynor family (Photo courtesy Vincent Gaynor)They’ve taken the clan to Disney World and to the Bahamas to swim with dolphins. Their youngest, who’s 8, lies beside Sophia on her bed and watches movies with her.
Now 15, Sophia had her longest-ever hospitalization in early 2024 when a virus caused her blood sugar to plummet and triggered frequent seizures. She didn’t wake up for two weeks. Since then, she’s been weaker, her affect flatter.
Her parents say they don’t think about the future. “Our focus is that she’s happy, that there’s love all around her,” Catherine said. “It’s just day to day.”
The Gaynors have taken solace in the idea that, through Sophia’s Cure, their daughter has made a difference for all the children with SMA who came after her. “That was kind of our consolation prize,” Catherine said.
One of those kids turned out to be her cousin, Vincent’s sister’s son, who was diagnosed with SMA in 2023 and then treated with Zolgensma. He walked at 10 months and now races around. “That helped me, in part, feel better about what we did,” Vincent said.
He still bristles at the drug’s price, which he blames on the payouts hauled in by those at AveXis and now Novartis.
“All those people, they all came in at the 12th hour once the trial was funded and you had the breakthrough,” he said. “Once it was taken from us, it was all about greed.”
Do You Have a Tip for ProPublica? Help Us Do Journalism.
Kirsten Berg contributed research.
“This was a case where the charities and the government did everything to get this thing commercialized, and then it just became an opportunity for a bunch of people to make transformative, generational wealth,” said James Love, director of the public advocacy group Knowledge Ecology International.
In cars, pollution doesn't come from exhaust alone. It also comes from wear and tear on roads, tires, and brakes. According to new research, tiny bits of dust cast off by brake pads may inflict more harm than car exhaust.

Liz Goggin, a social worker with the Veterans Health Administration, took the offer to resign in exchange for pay and benefits through September. Then she learned her position was exempt.
(Image credit: Justine Kenin)
It’s a huge unmet need to prevent Covid infections and block transmission. A nasal spray vaccine has the best shot of achieving this goal, as we’ve seen in many experimental models of candidate vaccines. I’ve reviewed the topic, rationale, and progress previously at Ground Truths, but it has been awhile and there are some interesting new developments, along with concerns about the jeopardy of these program with the new US administration. While SARS-CoV-2 circulating levels are relatively low at the moment, that is not likely to last as the virus’s evolution marches on.
This week the Ocugen Phase 1 trial of an adenovirus-vector spike protein nasal vaccine was given the go ahead by the FDA. This nasal spray vaccine was already approved in India, with ongoing trials, and actually is a work product of the Washington University lab of Michael Diamond, out-licensed to Bharat Biotech in India. Now a US-based company (Ocugen) has proceeded with an application to get it FDA-approved here. That makes it the 6th Covid nasal vaccine to go into clinical trials in the United States.
Here is a Table that summarizes the 6 different nasal vaccines with ongoing trials in the United States.
Let me review the status of each of these:
Castlevax, a spinout/intellectual property from Mt. Sinai, Icahn School of Medicine in New York City, supported by Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA)/Project Nextgen with $34 million. The viral vector is a live, attenuated Newcastle disease (a para-myxo virus-induced disease in chickens with asymptomatic or only mild, self-limiting impact in humans) expressing a SARS-CoV-2 spike protein stabilized by 6-prolines (rather than 2 in the current mRNA shots) to amp up the immune response. A small Phase 1 trial was completed but not yet published, yet data were available to BARDA. A Phase 2 randomized trial of 10,000 participants, half getting the nasal vaccine and half assigned to a shot, is in progress. A recent publication showed a single nasal vaccine administration completely blocked transmission of multiple variants of SARS-CoV-2 (including recent ones like KP.2) in 2 animal models (hamsters and mice). Interim results of a Phase 3 trial conducted in Mexico with this nasal vaccine showed comparable results as an intramuscular shot, but not published. A 4,000 participant randomized trial is underway in Thailand. Exact status of the US large trial enrollment is unclear other than data provided at clinicaltrials.gov.
Codagenix completed a Phase 1 trial of 48 participants with its live, attenuated SARS-CoV-2 virus that indicated it elicited solid immune response. The vaccine has an ongoing large randomized trial supported by the World Health Organization SOLIDARITY clinic trial consortium, and has an ongoing Phase 2B trial in the US. It is supported by BARDA/Project NextGen.
Cynavac/Blue Lake, supported by BARDA/Project Nextgen with $40 million recently started a Phase 2B 10,000 participant randomized trial on December 5, 2024. Expected to complete enrollment by June 2026, and final completion in 2027. It is a double-blind, randomized trial comparing this parainfluenza viral vector delivery of the spike protein vs Moderna’s intramuscular shot. The primary endpoint is prevention of Covid infections.
National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) has a Phase 1 ongoing trial of a live, attenuated parainfluenza virus with 6P spike protein (6P proline substitution reviewed in prior post) at Johns Hopkins in 2 sequential doses, open label, 27 participants, started enrollment in 2023 and should be complete by now, yet results are unpublished..
National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases has a Phase 1 ongoing trial of a murine pneumonia virus vector spike protein (2P) that is supported by BARDA/Project Next Gen after rodent and non-human primate models showed a strong immunogenicity response and lack of safety issue. The trial is enrolling 60 participants, open-label, dose escalation as a booster to shots.
Ocugen is bringing back to the US the Bharat Biotech nasal vaccine that was conceived and had preclinical assessment by Washington University, and subsequently tested in clinical trials and made commercially available in India. As mentioned at the top of this post, just this week FDA approved the go ahead with a Phase 1 trial. It will enroll 80 adults testing 2 different doses of the nasal vaccine and an orally inhaled version. In India, a Phase 3 randomized trial in over 3,000 participants was published demonstrating a robust immune response as a booster compared with a shot. The clinical outcomes of that trial have not yet been published.
Other Related Programs
There are many other nasal Covid vaccines that are being assessed in other countries. For example, In JCI Insight, in China, 128 health care workers were given 2 doses of a nasal vaccine spray, one month apart, at the end of 2022, after prior vaccination. The vaccine is an adenovirus vector that is replication-incompetent, directed against the Omicron BA.1 spike. As it turns out, this nasal vaccine induced more than 50-fold increase in spike-specific IgA secretory antibodies, indicative of achieving potent mucosal immunity. This was seen and consistent against 10 different variants of SARSCoV2.
Moat Bio has a Covid nasal vaccine program in Australia; the initial work was done by Mayo Clinic. There are also early clinical trials in Finland (Rokote), the Netherlands (Intravacc), Singapore and Switzerland (ACM), and they are available in Russia, Cuba, and Iran but without published data that I have seen or could find.
On the related topic of achieving mucosal immunity via oral, inhalation Covid vaccines, there is Aerovax, given as an aerosol. It uses a adenovirus vector but instead of only expressing the spike protein S1 subunit, it also expressed the nucleocapsid and RNA polymerase genes. It is proceeding with a Phase 2 trial in 350 participants. It is a Canada-based program led at McMaster University. Many other inhalation Covid vaccine programs are ongoing in China, Israel (Oravax), Australia (Vaxine), Germany, and other countries.
Vaxart recently released its interim results of a Phase 2B randomized, double-blind oral vaccine pill and is moving ahead with a 10,000 participant trial. It isn’t clear how this route-induced mucosal immunity compares with nasal or inhalation strategies.
Meissa, a spinout of Emory University, had very encouraging results in multiple experimental models, including nonhuman primates using a nasally delivered attenuated RSV vector expressing the spike. But the company ran into financial troubles and has not been able to move into clinical trials.
GeoVax is moving forward , supported by BARDA/NextGen, with a vaccine shot (not oral or nasal) specifically to rev up the immune response in immunocompromised individuals
Related Publications or Preprints, Not Covid-Specific
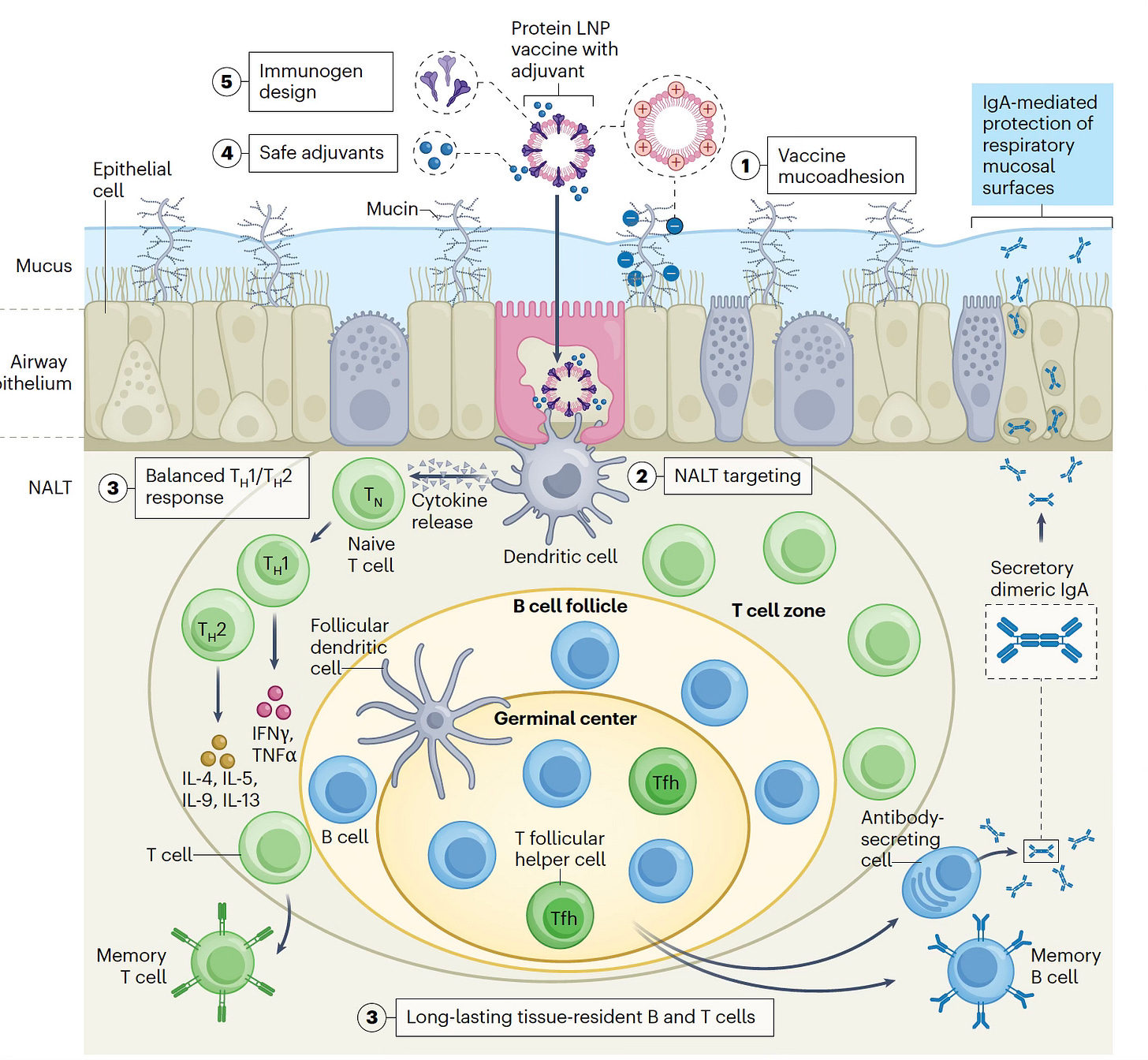
—The challenges of achieving a durable immune response with a nasal vaccine (Figure) were succinctly laid out in this recent Nature Biotech essay.
—Report of an effective nasal vaccine vs flu in experimental models, and another example here.
—A self-amplifying RNA nasal vaccine was highly effective against H5N1 and H7N9 influenza in mice and ferrets, but intramuscular shots were not.
Summing Up
It’s great that there are now 6 different programs with ongoing clinical trials in the United States to move Covid nasal vaccines forward, giving us multiple shots on goal (no pun intended) to have at least one that’s effective and safe. We’re far behind where we should be at this point, 5 years into the Covid era, because mucosal vaccines (nasal or oral) have never been a priority, like shots were with Operation Warp Speed. Specific funding for them was not approved by Congress, and it took the Project NextGen allocation to provide support for the 3 programs that are now furthest along—Castlevax, Cynavac, and Codagenix.
These programs are into large randomized trials, with a goal of enrolling 10,000 participants. It is hard to understand why they are categorized as “Phase 2B” since successful completion of a trial of this size would ordinarily be considered as definitive, Phase 3 evidence of efficacy, assuming the results were positive.
That brings up the first challenge. The levels of circulating SARS-CoV-2 are low now, which will slow enrollment (reduced concern and awareness) and the number of outcomes (prevention of infections, the primary endpoint of the trials). Support for the clinical trial infrastructure is the big expense of the programs (hundreds of millions of dollars kicks in) that will only increase with slower, longer duration of trial execution.
The second challenge is touched on in the Nature Biotech piece above. Even though we’ve seen multiple Covid vaccines protective against infections in animal models of mice, hamsters, and nonhuman primates, proving that in people, with durable protection (such as a vaccine spray every 3 or 4 months), remains to be seen. I am optimistic this goal will be achieved for SARS-CoV-2 from the totality of evidence we have so far, but we’re at least a year away from the read outs from the programs that are the furthest along. The only way this delay could be reduced would be for Bharat Biotech’s trial data of clinical efficacy (not just immune response) to be made available (we still haven’t seen it and, in general, publications of all these programs have been scant or markedly delayed) and used to support Ocugen’s FDA application. However, that is quite unlikely. Note I have only highlighted the 6 programs in the US, since nasal vaccine programs in other countries are unlikely to get authorized here without trials conducted in the US.
Perhaps the most formidable and third challenge is the continued US support for the Covid nasal vaccines. The 3 programs that are in late stage trials are all supported by BARDA/Project NextGen. The two Phase 1 trials at NIH are also government subsidized. With the new administration, and potential disregard for continued waves of Covid in the future, along with a policy that does not support any vaccines, no less reduced NIH support for research, there is serious jeopardy of all of the work toward Covid nasal vaccines. Withdrawing support for these programs would essentially pull the rug out for any hope to have a nasal Covid vaccine in the US over the foreseeable future.
***************************************
Thanks for reading and subscribing to Ground Truths.
If you found this interesting please share it!
That makes the work involved in putting these together especially worthwhile.
All content on Ground Truths—its newsletters, analyses, and podcasts, are free, open-access.
Paid subscriptions are voluntary and all proceeds from them go to support Scripps Research. They do allow for posting comments and questions, which I do my best to respond to. Many thanks to those who have contributed—they have greatly helped fund our summer internship programs for the past two years.